Im my current working profile we are adapting k8s with Istio. Istio as service mesh offers quite a range of services like Traffic management, security, telemetry etc. Getting a hands-on experience of all of these features is a must before we start adapting them in our applications. With the goal of getting to know Istio better I started configuring it for my sample set of applications.
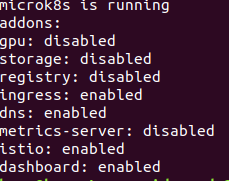
I have been using Microk8s for a while now and I must admit I like smaller footprint and convinent setup it provides for the support packages. We can find out the list of supported packages by using microk8s.status.
Setup
The command prints out which supported packages are enabled / disabled. Enabling Istio was a cake walk with the following command :
microk8s.enable istio
Well this is quite diffrent if we consider Istio administration in production environments. There we would like to do setup via Helm. I didn’t want to add the Helm complexity here.
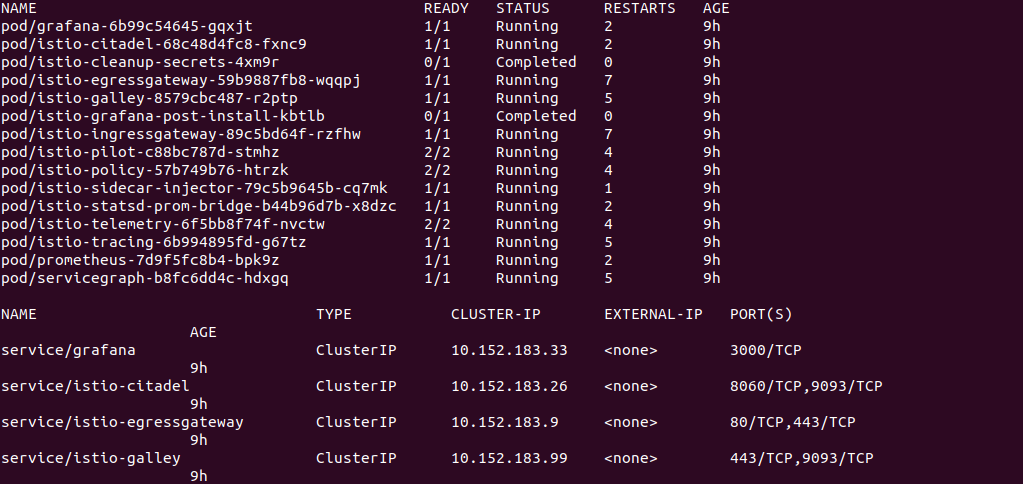
The above commands deploys complete Istio suite of services. We can verify by determining components deployed in istio-system namespace.
microk8s.kubectl get all -n istio-system
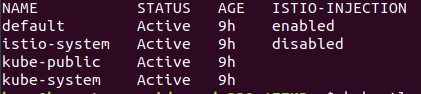
Now we need run our services with Istio Proxy. This can be done by either selecting a deployed application and then injecting Istio proxy in the respective pods. Alternatively we can add istio-injection label to a namespace and this will inject proxy in all pods running under the said namespace.
microk8s.kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=true
To remove the label run the following command :
microk8s.kubectl label --overwrite namespace default istio-injection=
Once a namespace is enabled for Istio injection all new Pods running in the namespace will have the settings enabled. So I wanted to enable it for my spring-greetings service. (This could be any other application deployed in your k8s custer). I deleted the running pod for spring-gs.
microk8s.kubectl get pod
microk8s.kubectl delete pod spring-gs-555cd5cd47-i786d
K8s created a new pod for the spring-gs deployment. Now lets verify if istio proxy has been injected by looking into Pod.
microk8s.kubectl get pod
microk8s.kubectl describe pod spring-gs-555cd5cd47-h852d
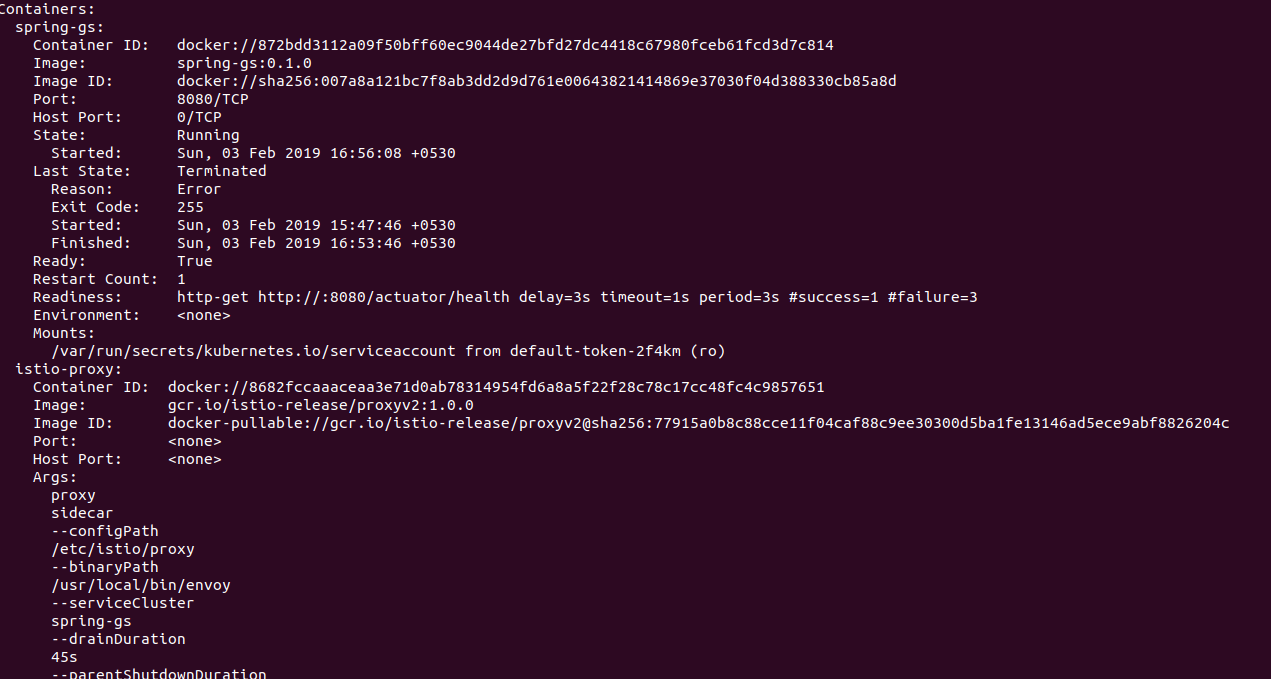
We can see that the new pod contains reference to Envoy proxy and the related Istio configuration. This can also be verified by using istioctl CLI :
microk8s.istioctl proxy-status

We can see a spring-gs proxy with SYNC status. Thats all is required to configure an application in Istio ecosystem.
Telemetry
In this post We will look at tha telementry feature offerred by Istio. The proxy captures load of metrices which are availbe on the Istio Dashboard. The dashboard ia available via garafana service. so lets determine the address of garfana service microk8s.kubectl get svc -n istio-system and do a lookup on 3000 port.
Lets now hit our service in a loop :
while true; do curl "http://10.152.183.60:8080/"; sleep 1; done
The pilot dashboard will should the request load.
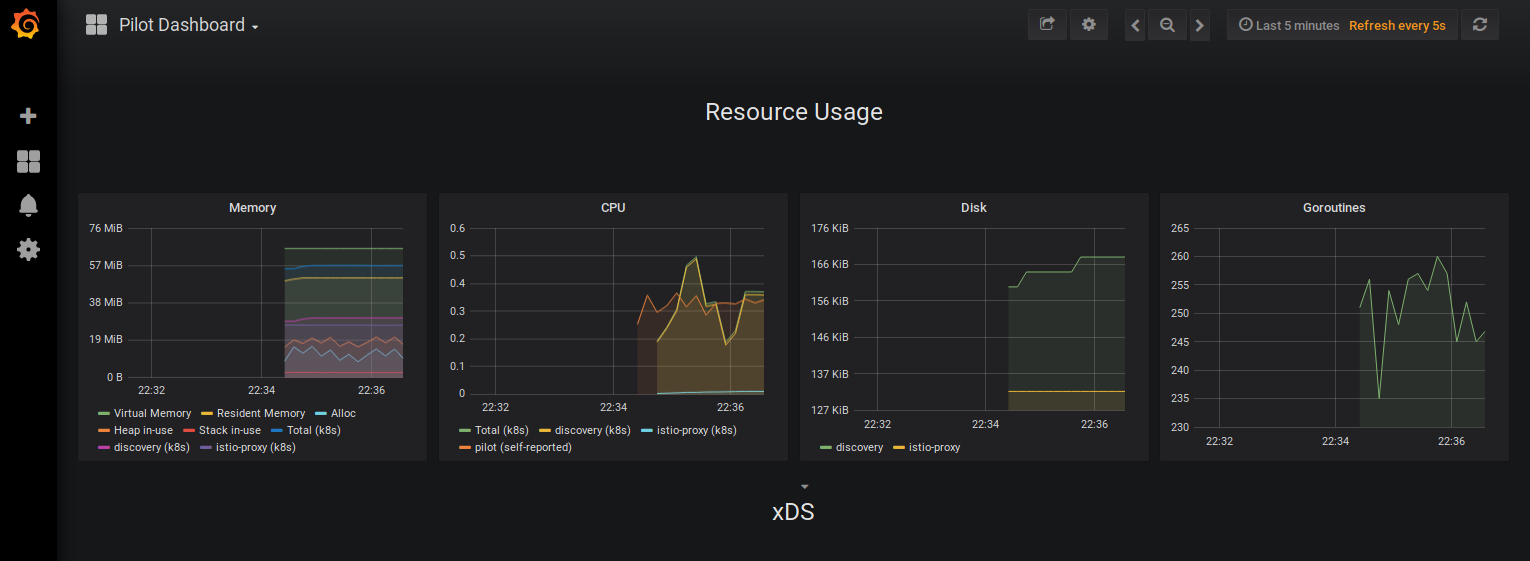
Istio dashboard looks quite informative. There are several reports in the dashbaord displaying the latest set of captured metrices.